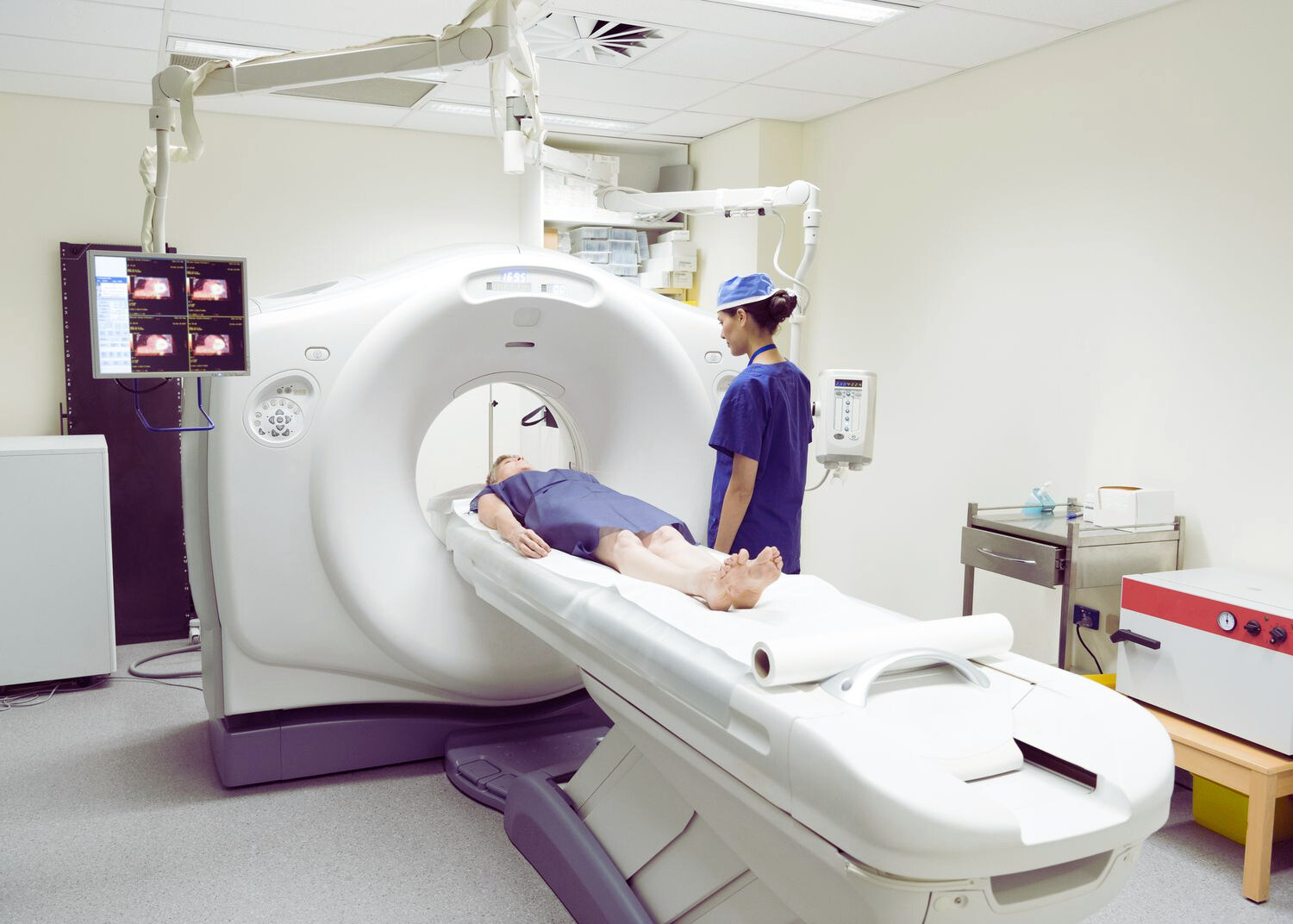
PET CT Scan have become an essential component of current medical diagnostics. This powerful imaging technique combines the strengths of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and X-ray Computed Tomography (CT) to provide a unique glimpse into your body. By revealing both cellular activity and detailed anatomical structures, PET CT scans offer invaluable insights for diagnosing and managing a wide range of health conditions. However, with various types of PET CT scans available, navigating this world can feel like venturing into a maze. This blog aims to be your guide, demystifying the different PET CT Scans and their specific purposes.
Understanding The Power of PET CT Scans
Let’s break down the technology behind PET CT scans. PET utilizes radiotracers, tiny amounts of radioactive materials injected into your bloodstream. These tracers target specific molecules or processes within your body. For instance, the most common radiotracer, Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), mimics sugar. Cancerous cells, with their high metabolic activity, tend to “gobble up” more FDG. A PET scanner then detects the emitted radiation from the accumulated radiotracer, creating a functional image that highlights areas with increased activity.
Here’s where CT comes in. A CT scan uses X-rays to generate detailed cross-sectional images of your body’s anatomy.Combining functional information from PET with anatomical data from CT results in a stunning fusion image. This allows doctors to pinpoint the exact location of increased activity within your body, leading to a more precise diagnosis and treatment plan.
The All-Rounder: FDG-PET CT Scan
The FDG-PET CT scan, which employs the FDG radiotracer, is the most prevalent type. Its versatility makes it a vital tool in various medical scenarios:
- Cancer Detection and Staging: FDG-PET is highly effective in identifying cancerous lesions, even in their early stages. It can also help determine the extent of cancer spread (staging), crucial for guiding treatment decisions.
- Treatment Monitoring: FDG-PET scans are invaluable in monitoring the effectiveness of cancer treatment. By tracking changes in FDG uptake, doctors can assess if a treatment is working or if adjustments are needed.
- Relapse Detection: FDG-PET scans can also be used to detect cancer recurrence after treatment completion. Early detection allows for rapid action, which may improve outcomes.
Beyond Cancer: Exploring Specialized PET CT Scans
While FDG-PET excels in oncology, the world of PET CT scans extends far beyond cancer diagnosis. By using different radiotracers that target specific functions within the body, doctors can delve deeper into various medical conditions:
- Cardiac PET Scan: This specialized scan utilizes radiotracers to assess blood flow and heart muscle function. It plays a crucial role in diagnosing coronary artery disease, evaluating the extent of heart damage after a heart attack, and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for heart failure.
- Brain PET Scan: Brain PET scans explore brain function and metabolism. They are valuable for diagnosing neurological conditions like dementia, epilepsy, and Alzheimer’s disease. By studying specific tracers that target neurotransmitters or glucose metabolism in the brain, doctors can pinpoint areas of abnormal activity, leading to a more accurate diagnosis.
- PSMA PET Scan (Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen): This scan specifically targets the PSMA protein, often overexpressed on prostate cancer cells. It is particularly beneficial for diagnosing aggressive or recurring prostate cancer, especially when conventional imaging techniques are inconclusive.PSMA PET scans can also assist stage prostate cancer and monitor treatment progress.
- DOTA PET Scan (Dopamine Transporter): This scan utilizes a radiotracer that binds to dopamine transporters in the brain. It plays a crucial role in diagnosing Parkinson’s disease and other movement disorders by revealing abnormalities in dopamine function within the brain.
- FDOPA PET Scan: This scan utilizes a radiotracer that targets the amino acid L-DOPA, a precursor to dopamine. It is helpful in evaluating patients with suspected Parkinson’s disease and other movement disorders, particularly those with atypical presentations.
Choosing The Right Scan For You
Here’s a simplified breakdown to help you understand which PET CT scan might be recommended for different scenarios:
- General cancer screening or monitoring: FDG-PET CT scan is the usual choice.
- Heart health evaluation: Cardiac PET scan might be recommended, especially if other tests are inconclusive.
- Brain function assessment: Brain PET scan is often used to differentiate between various neurological conditions.
- Prostate cancer diagnosis or monitoring, particularly for aggressive or recurring cases: PSMA PET Scan might be beneficial.
- DOTA PET scans or F DOPA PET scans may be useful for diagnosing movement disorders, particularly Parkinson’s disease.
Remember: This is a general overview. It’s crucial to consult with your doctor for personalized advice regarding the most suitable PET CT Scan for your specific situation. They will consider all the relevant factors and discuss the potential benefits and risks of the scan with you.
Beyond The Scan: What To Expect ?
Your doctor will provide detailed instructions prior to the PET CT scan. This might involve dietary restrictions or fasting for a specific period, depending on the radiotracer used. The scan itself is often painless and lasts about 30-60 minutes. You’ll be injected with the radiotracer and then lie down on a scanning table that moves through the PET scanner.Following the scan, you may be advised to drink plenty of water to flush any residual radiotracer from your system.
Understanding The Results
The PET CT scan data will be interpreted by a trained physician, most likely a nuclear medicine expert. They will analyze the combined PET and CT images, considering areas of increased activity on the PET scan and their corresponding location on the CT scan. In a follow-up session, Your physician will explain the findings to you.
A Powerful Tool, Not A Definitive Answer
It’s important to understand that a PET CT scan is just one piece of the puzzle. Your doctor will use the findings of other tests, your medical history, and a physical examination to make a diagnosis and propose the best course of therapy. In some cases, additional tests might be needed for confirmation.
Conclusion
Different PET CT Scan offer a powerful tool for diagnosing and managing various medical conditions. According to the rnmcenter from cancer to heart disease to neurological disorders, this technology provides valuable insights into your body’s function. By understanding the different types of PET CT scans available and their applications, you can feel more empowered when discussing this imaging test with your doctor. Remember, open communication with your doctor is key to understanding your specific needs and ensuring you receive the most appropriate care.